| Start | |
|---|---|
| Step # | |
| 1 | Generates Key Pair |
| 2 | Generates Symmetric Key Session |
| 3 | Sends Hashed Identity |
| 4 | Verifies Identity |
| 5 | Sends Challenge Message |
| 6 | Responds With Correct Challenge |
| 7 | Authentication Successful |
| 8 | Secure Session Key Exchange | End |
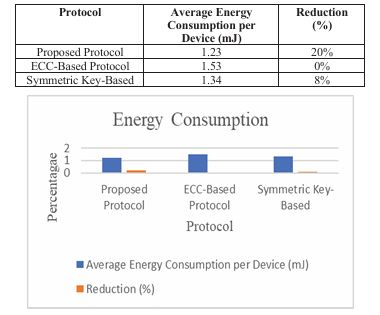
Many IoT devices are too weak to run heavy authentication or encryption protocols. One solution is a lightweight authentication system that mixes elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) for key exchange with symmetric encryption for actual data transmission. This hybrid approach made a lot of sense for ECC offers a strong security with small keys, while symmetric encryption is fast and energy-efficient. They tested their protocol on a simulated network of 100 IoT sensor nodes using real sensor data from the Intel Berkeley Research Lab. Compared to other authentication methods, their approach reduced energy use, authentication time, and communication overhead pretty significantly.
| Start | |
|---|---|
| Step # | |
| 1 | Generates Key Pair |
| 2 | Generates Symmetric Key Session |
| 3 | Sends Hashed Identity |
| 4 | Verifies Identity |
| 5 | Sends Challenge Message |
| 6 | Responds With Correct Challenge |
| 7 | Authentication Successful |
| 8 | Secure Session Key Exchange | End |


N. T and L. R, "Designing a Lightweight IoT Authentication Protocol for Resource-Constrained Devices," 2024
International Conference on IoT, Communication and Automation Technology (ICICAT), Gorakhpur, India, 2024,
pp. 962–966, doi: 10.1109/ICICAT62666.2024.10923434.