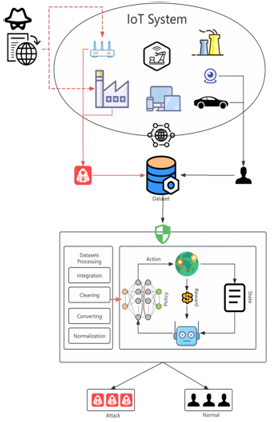
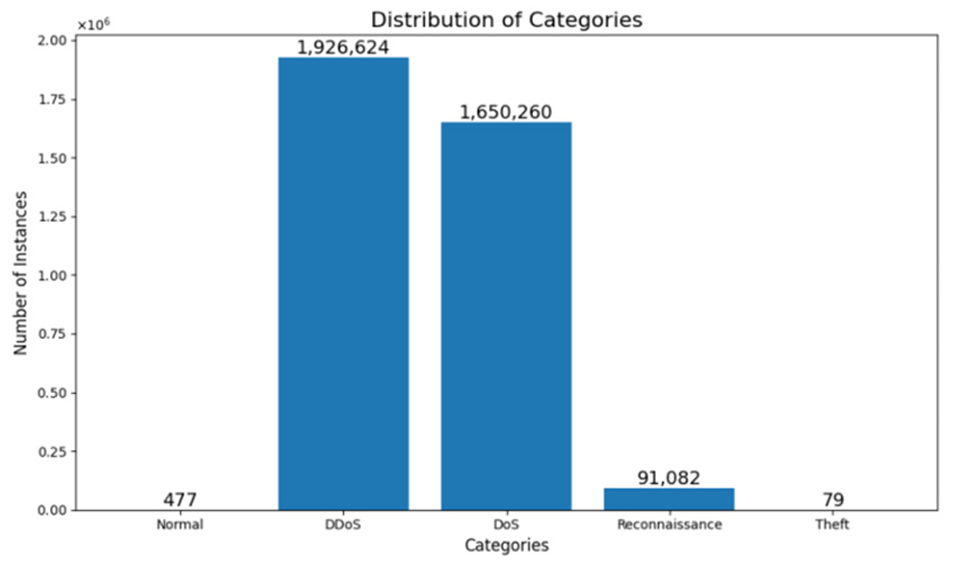
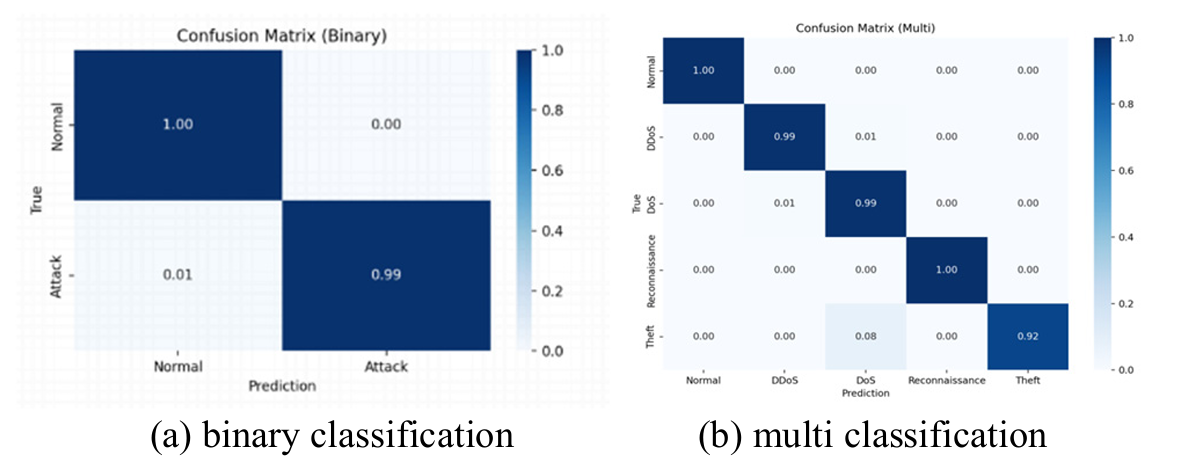
IoT devices are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks because they don’t have strong computing resources or storage. Traditional intrusion detection systems don’t keep up well with new attacks. Introducing a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) model that can automatically learn how to detect both common and rare attack types. One thing that this system uses is the use of a dynamic reward function, which essentially gives the model different rewards depending on how difficult a sample is to classify. This helps the system pay more attention to attack categories that don’t appear often in the dataset.



K. Ren, L. Liu, H. Bai and Y. Wen, "A Dynamic Reward-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning for IoT Intrusion Detection,"
2024 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Communication and Networking (ICN), Shenyang, China, 2024,
pp. 110–114, doi: 10.1109/ICN64251.2024.10865958.